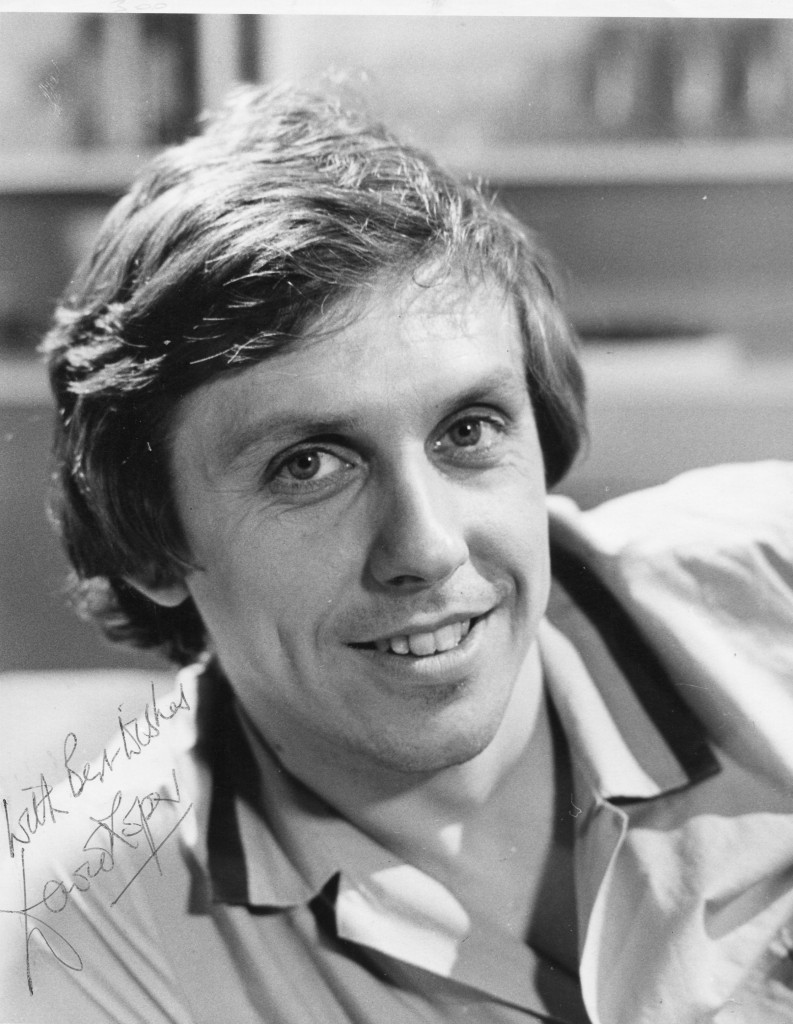
Many things are ‘wonderful’ in Saeed Jaffrey’s life, and quite a few things are ‘wonderful-wonderful’ (particularly the great actors he’s worked with, like Gladys Cooper, Sybil Thorndike and Ingrid Bergman).
After only a couple of hours, you can only feel fond of someone who’ll draw you a cartoon, sing you a song, and burst into tears at the memory of a friend.
We’re here to talk about his new series on Channel 4, Little Napoleons. But straight after the Toucan story, Jaffrey is on to a second: ‘Similarly, what I was going to say . . .’ Quite ordinary events take on the dimensions of a fable. ‘By the way, remind me . . .’ he says. ‘I’ll come to that later on. Lovely story.’
In Little Napoleons, in which Jaffrey co-stars with Norman Beaton, two rival solicitors become local councillors. Written by Michael Abbensetts (also responsible for Empire Road), it’s a comic insight into north-London politics which gives two old pros a roadworthy vehicle for their talents. Little Napoleons has a political edge, but Saeed Jaffrey doesn’t worry about politics. He looks blank at a standard question about the representation of Asians on television. He trusts his heart, he says, and (pointing a finger to the sky) the Governor.
The Governor has looked after him well: Jaffrey has made more than 70 films for Bollywood – the Indian film industry – sometimes doing three or four parts in a day for what he refers to as ‘Bombay cinema rep’. The Hindi films have taught him to be a quick learner. ‘You don’t have any credibility unless you are working on 12 films at the same time.’
Like Roshan Seth (last seen in Britain in The Buddha of Suburbia), Saeed Jaffrey has two careers: he’s well-known in Britain, and he’s huge in India. These two actors, who appeared together in Gandhi and My Beautiful Laundrette, in fact seem like opposites. While Seth is dry, detached, angular, Jaffrey is moist, engaging, round: he leaks expressiveness from every pore.
The day before the interview Jaffrey had been at the press screening of Little Napoleons. He was sitting in the same row as me, but further along, and although his figure was obscured, I could see his hands dancing in the air as he talked. He has quite a repertoire of hand gestures. There’s the stately sweep of the palm, the defiant index finger that precludes any objection, and the equivocal fluttering of fingers as if he’s practising scales. Watching Little Napoleons you see that he almost doubles the size of his role by giving his fingers a lot to say.
He’s a small man with a large physical presence: he has immaculate silver hair, a glint of cunning in his eyes, and a cartoon-like nose. Whether in Tandoori Nights, The Jewel in the Crown, The Far Pavilions or Staying On, Jaffrey has a Dickensian skill for investing self- importance, greed or slyness with a fullness of feeling that makes them sweetly human.
He’s been an actor for nearly 40 years. ‘I’m a Capricorn,’ he says, with deliberation. ‘The years up to the age of 40 are Capricorn’s apprenticeship years, when you get to know love. Life. Letters. The world. After that comes achievement and recognition. Which is what we want. Like Ismail Merchant.’ His eyes light up. ‘I told you about Ismail Merchant? Introducing him to James Ivory?’ (No.) ‘No?’
And he’s off: explaining how he and his first wife knew a man who was very talented and very sensitive, but who was useless at selling himself. But they also knew another man who was ‘Sammy Glick from Bindi Bazaar in Bombay’. A man who could sell anything.
One night the Jaffreys got the two of them round for dinner. Yes: ‘Within a week Merchant Ivory was born.’ He beams, raises his glass. The wine glasses clink. ‘Cheers. God bless.’ Salesmanship and sensitivity: there’s a quite a bit of Merchant and quite a bit of Ivory in Saeed Jaffrey.
His career started in Delhi in the mid-Fifties with All-India Radio. Through the job (‘which paid for the YMCA room’) he met artists and writers: the musician Ravi Shankar, the writer Khushwant Singh, and his first wife, Madhur, the actress, who later became a television cook (that’s another story). They married in 1958, had three daughters (one of whom is an actress) and divorced in 1966. His second wife, Jennifer, is a casting director and his agent (‘so wonderful, so tough’). In Delhi, Jaffrey started the Unity Theatre, performing Wilde, Shaw, Priestley. Why English plays? ‘I was much more comfortable with the English language.’ His father, Dr Hamid Hussain Jaffrey, had been a medical officer in Uttar Pradesh, which meant the family moved somewhere different in the area every three or four years.
‘I was exposed to a Muslim school, so I learnt Urdu. I was exposed to a Hindu school, so I learnt Hindi. I was exposed to a Church of England school, so I got my Senior Cambridge certificate.’ Not only was he cosmopolitan, but he and his two brothers and sister had, he says, ‘the good fortune of coming from rather good aristocratic Mogul stock’.
More directly, he inherited several talents from his mother. ‘One was to paint and sketch. One was to write – which I do – in Urdu, Hindi, English. One was mimicry, acting.’
His first wife, Madhur, wanted to go to Rada. ‘I said to her, look, as a mark of my love, I’ll stand down, so there’s no competition, and I’ll go next year.’ Next year, however, there wasn’t a scholarship available, so he got a Fulbright scholarship instead to the Catholic University of America, in Washington DC (Jon Voight was a fellow student). When the scholarship ended Jaffrey had three hungry months in Washington with hardly any money. A classmate invited him over one evening for a meal. He thought: ‘Why wait for supper, man? Let’s go now.’ But, with Mogul pride, he took out his diary to see if he was free.
In America, he was both the first Indian to tour Shakespeare, and the first to appear on Broadway, where he played Professor Godbole in the stage version of A Passage to India. In the first scene Godbole gets to sing a song; Jaffrey decided to sing a raga, an evening puriya. (He tried it out, first, down the phone to Ravi Shankar.) He sings me the raga in the bar at Bafta, then quotes the Saturday Review, which said (with good reason) that when Jaffrey sings ‘we are no longer in the concrete jungle of New York but transported to an ageless and beautiful India’. At that time Jaffrey played mainly non-Indian characters, including the Charles Laughton role in Witness for the Prosecution. Later, when he came to England, ‘I said to myself it doesn’t matter if it’s a six-line part. If they offer it to you, take it – enrich it with your background, and everything – so much that people will never forget it. That became my religion.’
An example of a small part making a big point was the role of the punkah-wallah in a television series called The Regiment. In a single line he reversed, he says, the cliche ‘all wogs look alike’. When asked to identify the officer who has committed a rape, Jaffrey’s character declines, rolling his head and saying: ‘All sahibs look alike.’
The best directors he has worked for – Satyajit Ray (The Chess Players), Richard Attenborough (Gandhi), John Huston (The Man Who Would Be King) – have all been ‘gardeners’. They’ve nursed actors.
David Lean, who directed him as Hamidullah in A Passage to India, is not among them. Jaffrey offers to do a drawing of Lean. He scratches away for 10 seconds, starting at the mouth and nose, working up to the hair and round to the neck. ‘You can only do cartoons of people that you don’t like all that much.’ The pen is too thin, but no matter, the feeling is there. Only Lean, he says, could have reduced ‘my lovely Dame Peggy’ to tears.
Jaffrey appears to be equally vulnerable to directors’ cruelty. When he was rehearsing Captain Brassbound’s Conversion in Brighton in 1971 this ‘ageing queer director was giving me the hardest time possible’. The show’s star, Ingrid Bergman, went to his defence. ‘At rehearsals, God bless her soul, the great tigress protecting her brood rose to her five-foot-10- and-a-half height and said: ‘Will you get off Saeed’s back]’ ‘ He then does a vicious impersonation of a simpering director backing down.
‘She was lovely . . ,’ he says. ‘Another good thing she did, before she died . . .’ (He halts, then suddenly starts crying. Half a minute passes. He whispers.) ‘She was, she was, she was . . .’ Some friends of his had come from India and wanted to meet her. (He takes off his glasses and puts them on the table and his hands cover his face. He’s heaving with sadness.) He had sent a note backstage to Ingrid Bergman and the dresser had taken them round. His friends were thrilled.
Each word from Jaffrey is now a struggle. ‘But the cancer had started to rise. Her fingers trembled and I could see the black marks.’ Bergman couldn’t stay long, she had to go to the hotel. It was the last time he saw her. ‘Great lady,’ he says, still in tears. He recovers a little from the memory, then the storyteller takes over again, and he reaches out for the next anecdote. ‘Years later, I was walking down Oxford Street . . .’
“Independent” interview above can also be accessed online
here.



:quality(70)/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/irishtimes/S66M2LYCCD4N3A3ZFL6I2IHZM4.jpg)




























































